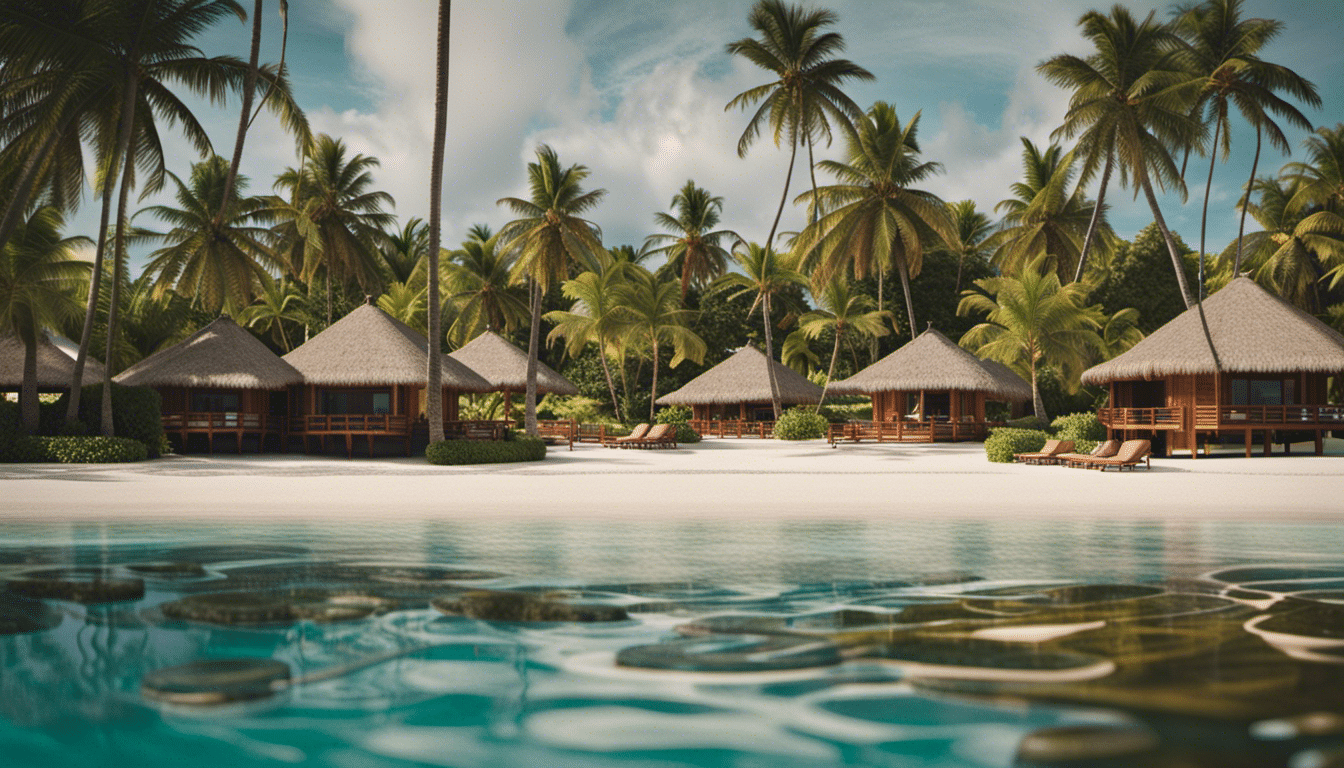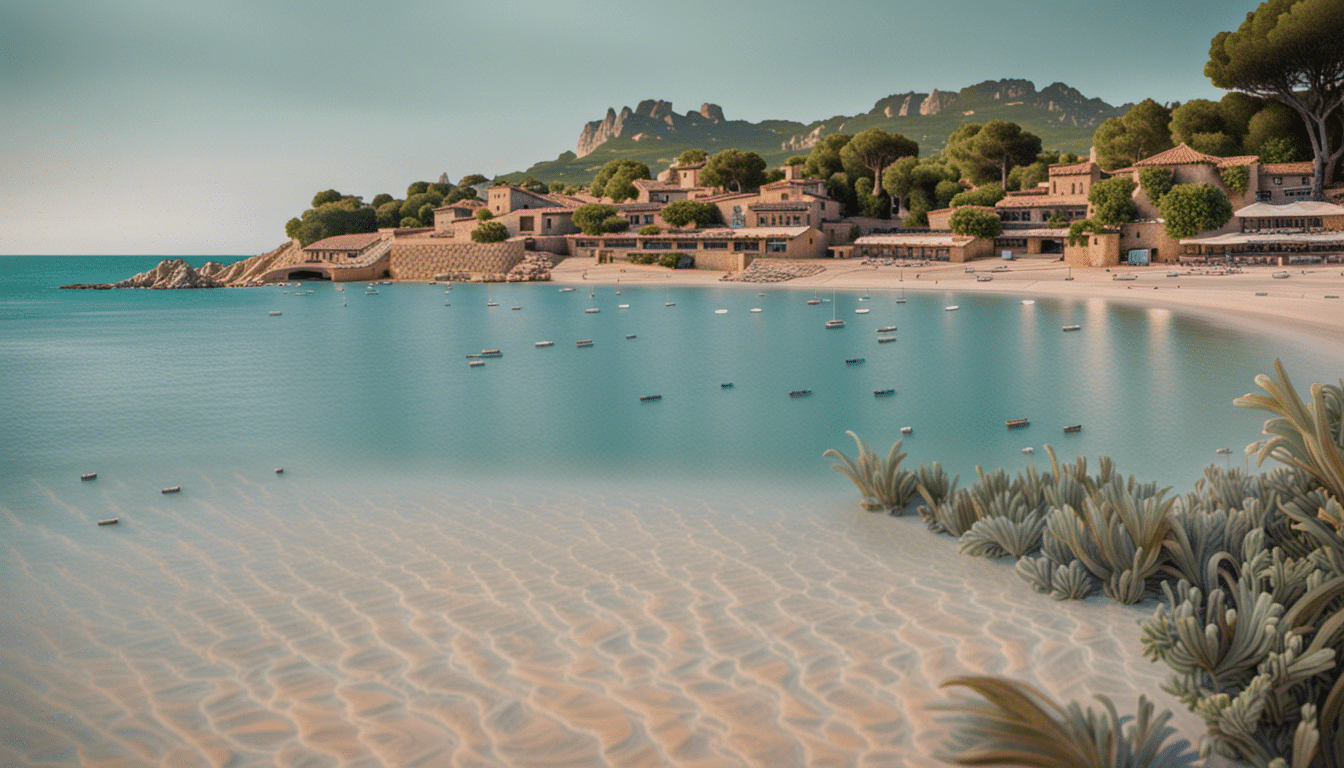Introduction: The geography of Tahiti
Tahiti is an island French Polynesia, located in the ocean peaceful, about 6,000 km away from mainland France. This 1,059 km² island is the largest of the Society Archipelago, of which it is the capital Pape’ete, and hosts the majority of the population of French Polynesia. In this article, we will explore the geography of Tahiti, from its area and latitude to its geological and climatic characteristics.
Area and latitude of Tahiti
Tahiti is approximately 45 km long by 17 km wide, making it one of the largest islands in French Polynesia. Its total area is 1,059 km², which is about 68% of the total area of the whole of French Polynesia. Tahiti is located at a latitude of 17.68 degrees South and a longitude of 149.43 degrees West.
Tahiti is made up of two main parts linked together by the Isthmus of Taravao. The part to the east of the isthmus is known as Tahiti Nui (big Tahiti) and the part to the west is called Tahiti Iti (little Tahiti). Geologically, Tahiti is a volcanic island whose formation dates back nearly 1.5 million years. Tahiti’s highest point is Mount Orohena, which rises 2,241 meters above sea level.
Tahiti, an island located in French Polynesia, is the largest and most populated of the Society Islands. Its total area is 1,043 km² and its population is over 190,000. This island is best known for its natural beauty, white sand beaches, crystal clear lagoons and green mountains. Mount Orohena is the highest point on the island, reaching a height of 2,241 meters.
In terms of geology, Tahiti is a volcanic island. It is made up of two distinct parts: Tahiti Nui (“big Tahiti”) and Tahiti Iti (“little Tahiti”), separated by the isthmus of Taravao. The nui is the larger of the two parts of the island and has the majority of urban infrastructure, while the iti is much less developed.
When it comes to Tahiti’s economy, tourism is one of the island’s main sources of income. Visitors are drawn to the white-sand beaches, lagoons suitable for scuba diving and swimming, and Polynesian culture, including traditional dance and music.
In addition, Tahiti has a rich cultural and political history. The natives of the island, the Tahitians, have lived on the island for thousands of years. They are known for their crafts, including colorful fabrics called pareos, wood and stone carvings, dancing and music. Tahiti also played a key role in the region’s politics, having been annexed by the French in 1880. Today, Tahiti is a territorial community of the French Republic in the same way as Corsica, Guyana or Martinique.
In conclusion, Tahiti is a mystical and beautiful island, offering a wealth of natural landscapes, Polynesian culture and fascinating history. This paradise island is a dream destination for tourists looking for adventure, relaxation and discovery. To learn more about Tahiti, consult the Larousse encyclopedia.
The climate of Tahiti
Tahiti enjoys a hot and humid tropical climate, with average temperatures ranging between 20°C (68°F) and 30°C (86°F) throughout the year. The rainy season extends from November to April, and the dry season from May to October. The average annual rainfall on the island is around 2,000 mm.
The vegetation of Tahiti
Tahiti is covered in lush vegetation, including dense rainforest that is home to a wide variety of animal and plant species. Common trees include coconut, mango, banana, and pandanus. Most of Tahiti’s native edible plants, such as taro and vanilla, are grown in the Papenoo Valley.
The beaches of Tahiti
Tahiti is famous for its white sand beaches and crystal clear waters. The most famous beach on the island is the black sand beach of Tahiti Iti, located on the south coast of the island. Teahupo’o Beach, also located on the south coast, is a world-class surfing spot and hosts an international surfing competition every year.
Tahiti Geography FAQs
How to get around in Tahiti?
Most visitors arrive in Tahiti by air at Faa’a International Airport, located in Papeete. On the island, transportation options include taxis, public buses, rental cars, and scooters.
What languages are spoken in Tahiti?
French is the official language of Tahiti, but Tahitian is also widely spoken on the island.
Some of the best activities in Tahiti include scuba diving, visiting botanical gardens, exploring archaeological sites, hiking in the mountains, exploring the surrounding beaches and islands, and learning about traditional Polynesian culture.
The geography of Tahiti is a rare wealth that deserves to be explored. Located in the South Pacific, Tahiti is the largest island in French Polynesia. It is made up of two distinct parts: Tahiti Nui, the larger of the two, and Tahiti Iti, smaller but more mountainous. The island’s geology is characterized by extinct volcanoes, steep cliffs and deep valleys. Fine sandy beaches and crystal clear lagoons are also part of the geography of Tahiti.
The relief of the island is the result of past volcanic and seismic activity. Papeete, the capital of French Polynesia, is located in the western part of the island, on the north coast. Towering mountains provide spectacular views of the city and the sea. Waterfalls and rivers are also present on the island, providing refreshing swimming spots.
The geography of Tahiti is also marked by the presence of neighboring islands. The islands of Moorea, Bora Bora, Huahine and Raiatea are located within a radius of a few hundred kilometers from Tahiti. They offer incredible landscapes and are popular destinations for tourists in search of escape.
In short, the geography of Tahiti is a treasure worth discovering. The mountains, beaches, lagoons and neighboring islands make Tahiti a unique destination in the world. If you want to know more about the geography of Tahiti, I invite you to consult this article from Etahititravel.com: The geography of Tahiti: a rare wealth. You will discover more details about the geology of the island and the tourist attractions it offers. Have a nice trip to Tahiti!
Are there any natural hazards on the island of Tahiti?
Tahiti is a relatively safe island, but there are a few natural hazards to be aware of. The waters surrounding the island are home to sharks, so it is important to follow safety guidelines when swimming and diving. Hikers should also exercise caution when exploring the mountains, as the trails can be slippery and difficult.
Conclusion
In summary, the geography of Tahiti is fascinating and diverse. This volcanic island in French Polynesia offers a wide variety of natural landscapes, from verdant mountains to white sand beaches and dense tropical forest. With its crystal clear waters, beautiful coral reefs and rich and exciting Polynesian culture, Tahiti is a must-visit travel destination for any discerning traveler.