Metropolitan France shares land borders with eight countries: Belgium and Luxembourg to the north, Germany and Switzerland to the east, Italy to the southeast, Monaco, Andorra and Spain to the south.
What are the TOM countries?

The overseas territory, or TOM, is a form of French overseas collection created in 1946 by the French Union, changing the level of colonialism.
What are foreign lands? Overseas, there are 12 territories which include foreign departments (Guadeloupe, Guyana, Martinique, Mayotte, Réunion) as well as New Caledonia, French Polynesia, Saint-Martin, Saint-Barthélémy, Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon, the south of France and the Antarctic, the…
Which country has the most Dom-TOM? When we talk about “France”, most of us forget the 12 outlying territories and territories of more than 200 islands and territories off the coast of more than 10,000,000 km2, the size of Canada.
Where is Dom-TOM?
There are four “foreign regions” (Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guyana and Réunion). Unlike metropolitan regions, ROMs consist of a single department, for example, regional departments.
Where is the DROM? Martinique, Guadeloupe, Guyana, Réunion and Mayotte form overseas departments (DROM); Wallis and Futuna, French Polynesia, Saint-Martin, Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon form foreign organizations (COM).
Which countries are part of the French departments and territories abroad? Overseas is 12 territories: Guadeloupe, Guyana, Martinique, Reunion, Mayotte, New Caledonia, French Polynesia, Saint-Barthélemy, Saint-Martin, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon, French Australia and Antarctica and the Wallis and Futuna Islands, for example nearly 2.6 million…
What are the statutes of overseas territories?

Overseas lands were given special status in consideration of their own interests within the Republic. The 1958 constitution includes both the diaspora, the departments and the territories. The word & quot; DOM-TOM & quot; it becomes common to mark all French territories abroad.
What are the different conditions abroad in France? I – Some territories have different conditions: Guyana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Reunion and Mayotte are the Departments and Regions (DROM). Saint Pierre and Miquelon or Tahiti are quasi voluntary foreign organizations (COM).
What is the situation abroad? The Ministry of Foreign Affairs (DROM) is governed by Article 73 of the Constitution. This standard applies to Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guyana, Reunion and Mayotte. The laws and regulations applicable in the French capital exist there as law (system of legislative recognition).
What do you call people who live in Charente-Maritime?
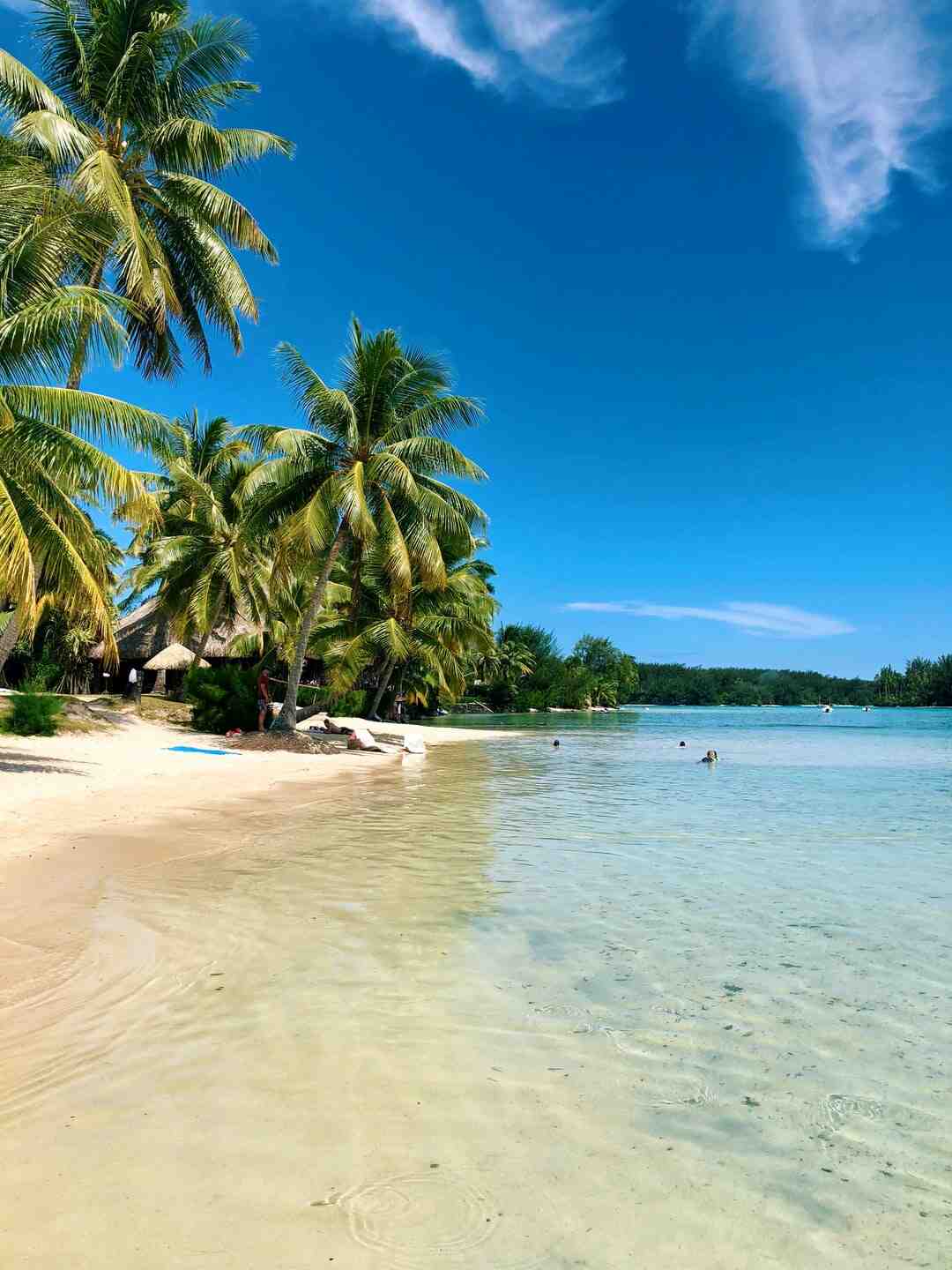

| NOT | department | Good |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | Calvados | Calvadosians |
| 15 | Cantal | Cantalous or Cantaliens |
| 16 | Charente | Charentais |
| 17 | Badda Charente | Charentais or Charentais-Maritimes |
What are people from the PACA region called? As the trend has become widespread, the commission seems ready to approve Pacaïens for residents of the province of Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur (PACA), because we have Domiens to designate people for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (DOM ).
How to make an international call?

To call abroad or in DROM, you must dial 00 (or + from the mobile) followed by the country number and the telephone number of your rapporteur.
How to call abroad without paying? Call for free or cheaper courier services. The replacement of mobile drivers is widely used: instant messaging services such as Skype, Whatsapp, Facebook Messenger, Facetime (iPhone and iPad), Viber or even Lebanon.
How to dial an external number? For example: 00 33 6 XX XX XX XX, if it is a foreign number: dial 00 (or), followed by the corresponding country of your rapporteur, then his number.
Which island to choose to live there?
If you are with family, be sure to choose an island with good health facilities and schools. This is particularly true in Reunion, Martinique, Guadeloupe and Guyana.
Where can you live on an island? From Gambolo or Siroktabe Island in Indonesia to the Virgin Islands of the Philippines, via Polynesia or Velassaru Island in the Maldives, it is unique in the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean that it is possible to find the most of the islands in the desert or almost deserted.
In which Dom-tom islands is it best to live? In this case, it is recommended to opt for departments and external territories equipped with good sanitary infrastructures, as well as a wide choice of schools. This is the case of Reunion, Martinique, Guadeloupe and Guyana.
What are the assets of the French territory?
France, thanks to its geographical location, offers a variety of landscapes and climates. It is a tourist and agricultural property. West, oceanic climate, very mild. – In the field, it is very, very hot on the mainland, it is hot in summer and winter is cold.
What are the characteristics of the French territory in Europe and in the world? Overall, France is considered a neutral country. With an area of 551,000 km², France is ranked 48th in the world (2nd European country)…. French climate.
- Western Ocean.
- Semi-continental in the east.
- Mediterranean Sea to the South.
How does France develop the potential of its communities? Development of French circles. French landscapes are French property. The terrain does not have many obstacles, which makes it possible to favor certain environments with economic activities, and others with tourism. French circles are very attractive and rich in resources.
Why is France called the metropolis?
It is also used in legal texts, especially those relating to the commemoration of slavery. A large city (from a Greek word meaning mother city) is originally the largest city in a country, region, region.
Why did we say more city to city? Although appropriate to the priority, Minister Eric Bareigts explains that the term “capital” appears in the Constitution, it will take constitutional reforms to eliminate it. She added that “l’Hexagone” would in fact exclude Corsica or the Breton islands. … And delete it by deleting the word from this text.
Who owns metropolitan France? France includes 96 departments in Europe, 5 overseas (Dom), Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guyana, Réunion and Mayotte (as of April 2011), as well as the following territories: New Caledonia, Polynesia French, the islands of Wallis and Futuna, the South and Antarctica…
Where are the French Overseas Territories located?
Guadeloupe and Martinique are located in the Lesser Antilles. These are islands off the coast of North America. Guyana is a landlocked country in South America, Amazonia and northern Brazil.
Where are the foreign lands? Outside the territory of the French Republic far from metropolitan France. They are located at both ends and illuminate more than three seas (Atlantic, Pacific, Indian).
Who are the DOMs and who are the TOMs? Thus, the foreign departments are four in number, namely Martinique, Guyana, Réunion and Guadeloupe. … The communes include Saint-Martin, New Caledonia, Mayotte, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna and Saint-Barthélemy.
What are you talking about in France? The word foreigner appeared to him during the second half of the 19th century and designated the colonizer. Inside France, since the 1930s, it has designated countries and territories under its control and the constitutions of 1946 and 1958 confirm this definition by triggering French states and territories outside Europe.
What are the characteristics of overseas territories?
Most of the outlying areas are volcanic islands in the tropical world, with severe relief, which are exposed to many natural hazards: earthquakes, volcanoes, tropical storms. They suffer from isolation due to incompatibility and distance, which makes communication difficult and costly.
What are the resources of foreign lands? This land is also characterized by unique cultures: Guyanese aerospace and the gold industry, fishing in the Indian Ocean, Caribbean sugar and sugar cane and Reunion, nickel in New Zealand. Caledonia etc
What are the different French territories abroad? 7 overseas communities (COM): New Caledonia, French Polynesia, Saint-Barthélemy; Saint-Martin; Saint Pierre and Miquelon; French Southern and Antarctic Lands and Wallis and Futuna.
What are the issues outside of France? The French diaspora faces unique challenges. Most of these lands face hazards related to tropical climates, including cyclones and hurricanes that sweep the islands of Guadeloupe, Martinique or Reunion.
Which territory is not part of the French overseas territories?
After the 1959 referendum, Wallis and Futuna chose to end the protectorate and become an outpost in 1961. After the referendum, Comoros was liberated in 1975 with the exception of Mayotte which voted to remain French.
What are the outer regions? The Ministry of Foreign Affairs (DOM) is the five territories of Guadeloupe, Guyana, Reunion, Martinique and Mayotte and many others. Each field has its own characteristics that offer different yields.
What are the French territories abroad? Guadeloupe and Reunion are both departments and provinces. Guyana, Martinique and Mayotte (using the power of overseas departments and regions as the “Department of Mayotte”) are three distinct communities.