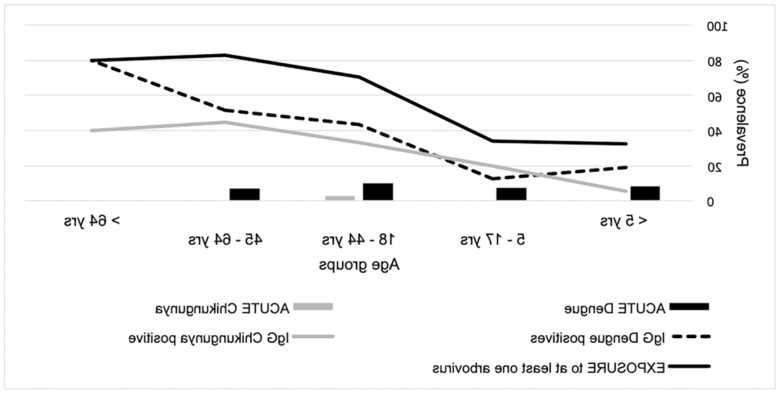
Symptoms are mostly flu-like (fever, headache, and pain in limbs) and appear within 3-14 days (average 4-7 days) after mosquito bites. Dengue fever affects infants as well as toddlers and adults.
What are the symptoms of dengue fever?

“Classic” dengue appears suddenly after 2 to 7 days of incubation with the appearance of a high fever, often accompanied by headaches, nausea, vomiting, joint and muscle pain and a rash of measles type.
Treatment There is no specific treatment or vaccination against dengue fever. Treatment is mainly symptomatic, including pain and fever. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated due to the risk of bleeding.
– Guava and red pepper juice: This remedy is very popular in Latin America against dengue fever and seems to have been proven there. Rich in vitamin C (known to promote the absorption of iron), the two foods relieve general disorders and help fight fatigue.
Dengue haemorrhagic fever, which accounts for approximately 1 to 2.5% of cases, is extremely severe: the fever persists and multiple gastrointestinal, cutaneous and cerebral haemorrhages occur.
Who dies from dengue fever? According to the WHO, 3.9 billion people in 138 countries are at risk of dengue infection in 2018. There are approximately 390 million infections worldwide each year, including 96 million patients, half a million hospitalizations (severe dengue fever) and 20,000 deaths, including a very high proportion of children.
How to relieve dengue fever pain?. In the case of classic dengue fever, we are responsible for relieving the patient of muscle aches, headaches and fever with painkillers and antipyretics such as paracetamol. Aspirin should be avoided at all costs as it increases the risk of bleeding. Bed rest is the rule.
How to treat dengue fever with plants? Artemisia annua is also recommended. Also mentioned was the infusion of cherry leaves with orange peel, two drops of peppermint essential oil with a sparkling cachet of efferalgan inside.
What is the difference between dengue fever and malaria?

Dengue fever
- strong headaches.
- retro-orbital bread.
- Muscle and joint pain.
- Nausea.
- You vomit.
- Lymphadenopathy.
- Itchy skin.
Severe malaria usually results from late treatment of uncomplicated malaria. This stage of the disease is defined by clinical or laboratory evidence of dysfunction of vital organs. Virtually all major malaria-related deaths are due to P. falciparum, but P.
There is no direct natural human-to-human transmission of the virus. Transmission takes place only through the vector mosquito. People with dengue are therefore not contagious by contact or sputter.
How is dengue fever produced? In most cases, dengue fever is mild and progresses spontaneously towards recovery: the symptoms disappear after the disappearance of the fever and the patient recovers without sequelae after a total duration of approximately one week.
What are the signs of severe malaria? They are manifested by a very high fever (41-42°C), severe neurological disorders with impaired consciousness (convulsions, coma, signs of meningitis) and various general symptoms (severe anemia, hypoglycemia, coagulation disorders and bleeding, liver and kidney damage ).
Where is dengue fever in Asia? In Thailand, more than 80,950 cases are recorded mainly in the provinces of Rayong, Petchburi, Rachaburi, Trad and Uthaitani. More than 91,000 cases have already been reported in Malaysia, including more than 230 deaths. The province of Selangor alone, to which Kuala Lumpur belongs, accounts for more than half of the cases.
What is the difference between chikungunya and dengue fever?

Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. The most common symptoms are fever and joint pain.
However, chikungunya, which is rarely fatal, can lead to complications in certain fragile people. Between 2005 and 2006, during the great epidemic in Reunion, more than 148 people were killed.
What is the treatment for dengue fever? There is no specific curative treatment or vaccination against dengue fever. Treatment is mainly symptomatic, including pain and fever. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated due to the risk of bleeding.
How is chikungunya treated? Treatment targets the symptoms of the disease, using painkillers such as paracetamol; Warning: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin are contraindicated during the acute phase of the infection, because their possible coexistence with the dengue virus carries a haemorrhagic risk.
What disease does the tiger mosquito cause? The Aedes albopictus mosquito (commonly known as the “tiger mosquito”) can transmit viruses such as chikungunya, dengue and zika. It is particularly present in the French departments of the Indian Ocean, where it triggered a very large epidemic of chikungunya in 2006.
What are the future risks associated with dengue fever?
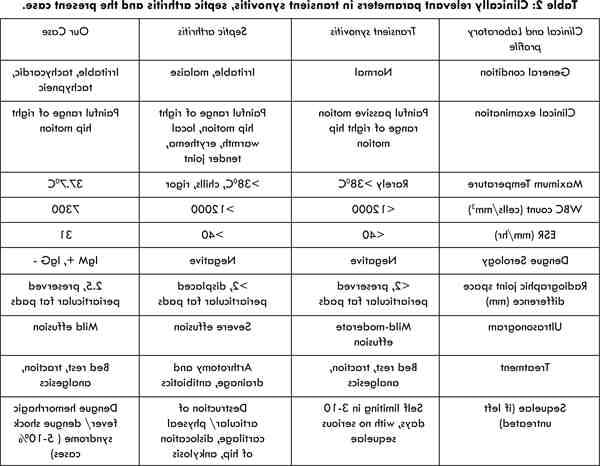
Complications – Dengue haemorrhagic fever The haemorrhagic form of the disease, which accounts for approximately 1% of dengue fever cases worldwide, is extremely serious: the fever persists and multiple bleedings often occur, in particular gastrointestinal, cutaneous and cerebral.
Treatment is symptomatic and is mainly based on taking paracetamol-based analgesics and rest. It is also recommended that people with dengue fever drink plenty of fluids.
What are the 4 types of dengue fever?. The four types of dengue virus are: DEN-1, -2, -3 and -4. These different types can circulate in the same region at the same time. When the virus is vaccinated in humans through mosquito bites, it enters the bloodstream and enters blood cells, where it replicates.
What is the incubation period for dengue fever? At the end of this extrinsic phase, this mosquito can transmit the virus by another bite and infect a new person. In dengue, the viraemic phase begins about 1 to 2 days before the onset of clinical symptoms and lasts up to 7 days afterwards.
What blood test for dengue fever?. The diagnosis of dengue fever is confirmed by the detection of the virus (virological examination) or its DNA (PCR technique) in the blood during the first five days of the disease or by specific antibodies (serology) which appear for five days after the disease epidemic.
How to recognize dengue hemorrhagic fever? Dengue hemorrhagic fever: in addition to fever, abdominal pain and vomiting, multiple bleeding occurs in the skin, mucous membranes and digestive tract. The general condition of the patient deteriorates with the risk of developing cardiovascular shock syndrome, which can be fatal.