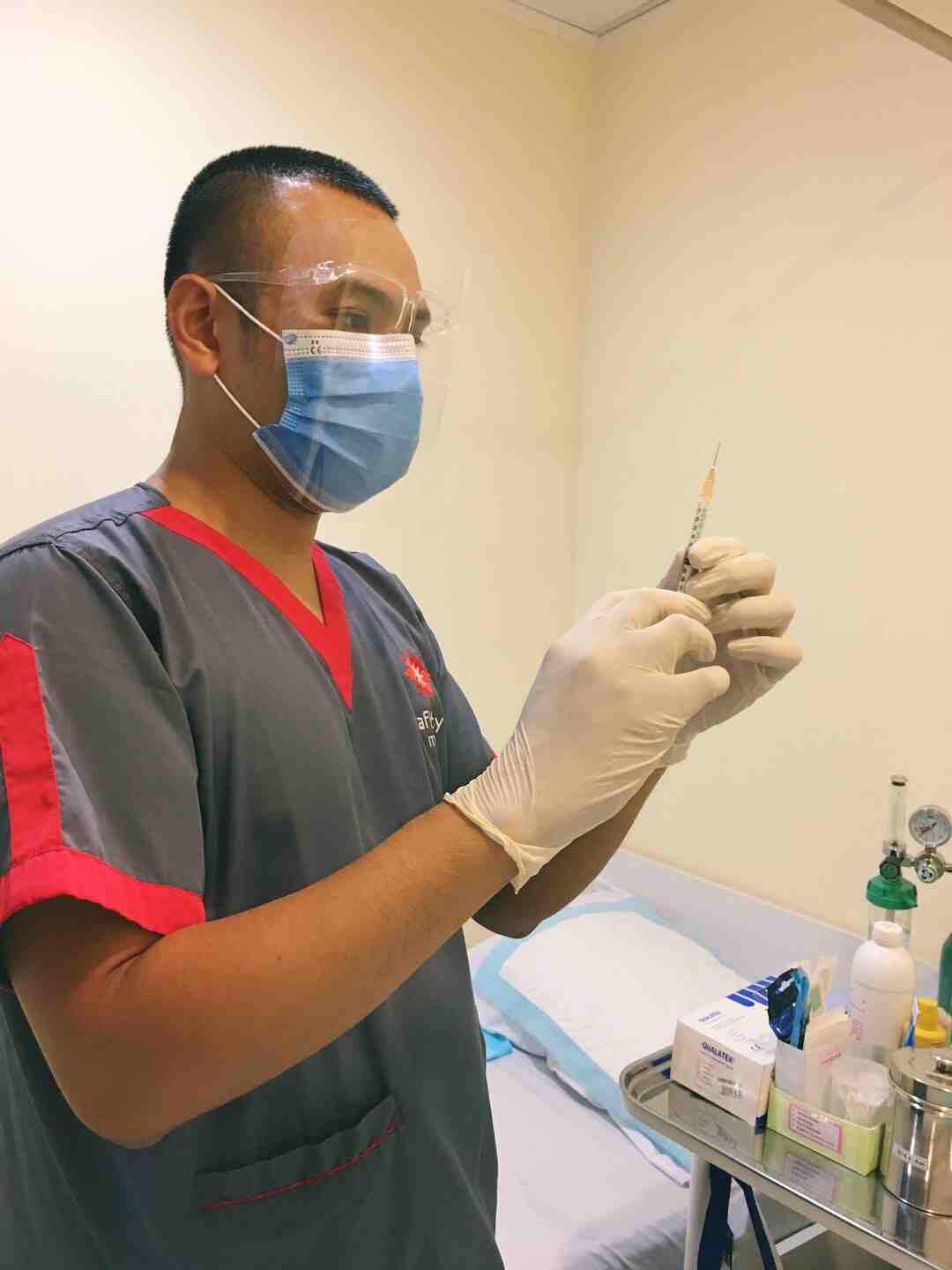
Good to know: There are also other non-compulsory vaccines that your doctor or the child’s pediatrician can offer, such as the vaccine against chickenpox (VARIVAX°) or against the rotavirus responsible for severe gastroenteritis in 6-month-old babies. (ROTARIX° ).
When to put the patch before vaccination?
In order to reduce the pain associated with the vaccination, the skin can be anesthetized by applying an anesthetic patch (EMLA patch) 1h30 before the time of the appointment. The patches can be glued on from the first vaccinations of life, at 2 months.
Where to put the 4 month vaccine patch? To place the patch in the correct place, it should be placed on the side of the thigh, upwards, under the diaper, where the pants can wrinkle. In medical jargon we speak of the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. It must be glued about 1 hour or even 1 hour 30 minutes before the shot.
Where to put the lidocaine patch? Hello, The patch is placed on the anterolateral side of the thighs; in the upper third. For the little ones, up to 2 months, apply 1/2 patch per thigh, for children over 3 to 11 months, one patch can be used per thigh.
Which vaccine every 5 years?

At 5-6 years old
- Whooping cough.
- Diphtheria.
- Poliomyelitis.
- Tetanus.
Which vaccine is mandatory at 6 years old?
Which compulsory vaccine is 25 years old? At 25, it’s time to get a booster against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis and whooping cough. For measles, mumps and rubella (MMR), you must have received 2 doses of the MMR vaccine during childhood to be well protected.
What are the vaccines to renew? COVID-19: All adults are eligible for vaccination as of May 31, 2021. Diphtheria, Tetanus, Polio, Pertussis: Booster at age 25. Diphtheria, Tetanus, Poliomyelitis: If the last recall of Diphtheria, Tetanus, Poliomyelitis, Pertussis is less than five years ago.
Video: Which vaccines for infants?
What were the mandatory vaccines before 2018?
Children born before January 1, 2018: vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus and poliomyelitis is compulsory.
What is the only mandatory vaccination in France? Child born before 2018 Compulsory vaccines are: diphtheria, tetanus and poliomyelitis (DTP). And for residents of Guyana, yellow fever, from 1 year. The holders of parental authority must ensure compliance with this obligation.
What are the 11 mandatory vaccines? Since 2018, there are therefore eleven compulsory vaccinations (source 2): diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, whooping cough, infection with Haemophilus influenzae b, hepatitis B, type C meningococcus, pneumococcus, measles , mumps and rubella are included in the vaccination schedule. for children born in…
Why don’t we do BCG anymore?

As Professor Daniel Floret, President of the Technical Vaccination Committee, also points out, other reasons explain the decision to no longer make BCG compulsory, such as “its effectiveness, which is not optimal, and its side effects far from be negligible.
What disease protects BCG? This is the so-called BCG vaccine, named after its inventors (Bacille Calmette and Guérin). Vaccination against tuberculosis mainly concerns children who are particularly exposed to the tuberculosis bacillus.
Since when is BCG mandatory? The child is saved thanks to the vaccine. It was then administered to a few hundred babies until 1924, before becoming widespread under the name of BCG (Bacille Calmette and Guérin). The BCG vaccine became compulsory in France from 1950.
Is the tuberculosis vaccine compulsory? Vaccination against tuberculosis is no longer compulsory. It is still recommended for some children.