Introduction to the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve
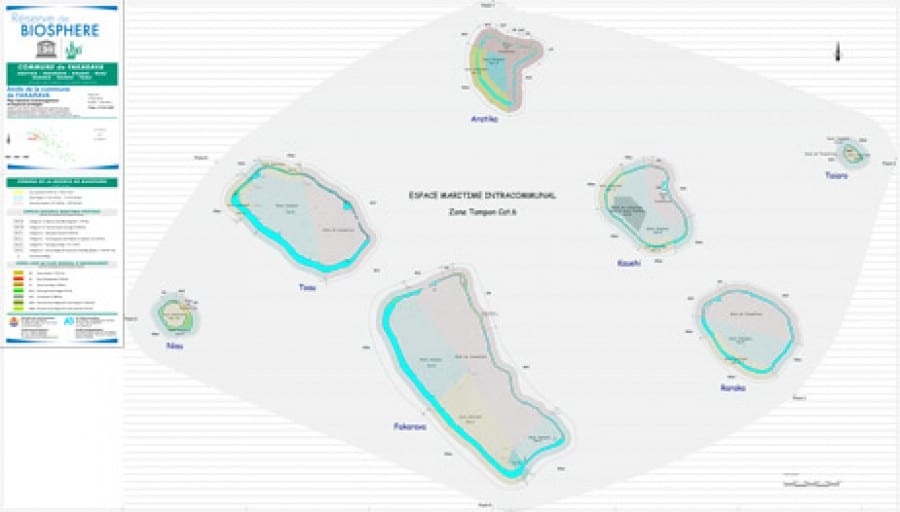
There Fakarava Biosphere Reserve is a protected natural area located in thearchipelago of the Tuamotu, in Polynesia French. Listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2006, this reserve encompasses a maritime area of nearly 5.7 million square kilometres, covering all the atolls of the common of Fakarava including Aratika, Kauehi and other atolls. Its main objective is to preserve the exceptional biodiversity of this region as well as the local ecosystems and cultures.
The ecological richness of the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve
The protected area of Fakarava to regroup in different marine and terrestrial ecosystems sheltering a great diversity of animal and plant species. The atolls, located in the heart of the Pacific Ocean, offer an exceptional setting for the observation of marine animals and birds. Here are some of the remarkable spaces that can be discovered within the reserve:
The atolls of Tuamotu are home to some of the richest and best preserved coral reefs in the world. These reefs form complex and interdependent ecosystems where fish, reptiles, crustaceans, echinoderms, corals and various plant species live side by side. It is possible to practice snorkeling or scuba diving to meet this incredible marine biodiversity.
The Fakarava Biosphere Reserve, located in the Tuamotu Archipelago in French Polynesia, is a veritable Eden of biodiversity. Listed in the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 2006, this protected area encompasses the atoll of Fakarava as well as six other atolls (Toau, Niau, Aratika, Kauehi, Taiaro and Raraka). Extending over an area of 6,675 km², it offers a precious refuge to a multitude of marine and terrestrial species.
The marine environment of Fakarava Biosphere Reserve is exceptionally rich. The crystal clear waters of the lagoons are home to treasures of biodiversity, including a wide variety of fish, unique corals, turtles, sharks, dolphins and whales. The atolls of Fakarava and its neighbor Rangiroa are also renowned for the beauty of their underwater landscapes and the density of their marine life, which makes them particularly popular with divers from all over the world. The coral formations here are of great diversity, offering a fascinating spectacle for both marine biologists and lovers of underwater exploration.
In addition, the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve plays a crucial role in the preservation of island ecosystems, ensuring the protection of plant and animal species that inhabit the emerged lands. Indeed, it is home to rare and endangered endemic species, such as the Kuhl songbird, the Tuamotu kingfisher or the Tuamotu redhorse. Tropical forests, coconut groves and white sand beaches are essential habitats for these species, which contribute to the ecological balance and the beauty of the landscapes.
The preservation and sustainable management of the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve are ensured by collaboration between local communities, researchers and land managers, thus guaranteeing respect and enhancement of the unique natural and cultural heritage that characterizes this Eden of biodiversity. . The involvement of local populations is particularly important, in order to ensure a balanced management of resources and to promote economic development compatible with the safeguarding of an exceptional ecosystem such as that of the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve.
The Fakarava Biosphere Reserve is a unique ecosystem located in the heart of the Tuamotu Archipelago, in French Polynesia. It has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2006, and its exceptional biological and cultural richness makes it both fascinating and precious. The particularity of this reserve lies in its biodiversity and its size: it extends over more than 400 km² and includes the atoll of Fakarava as well as six other atolls. “Protecting the Queen of the Polynesian Islands: the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve” is therefore an essential and urgent mission, both for the preservation of this unique biodiversity and for the sustainable development of the entire local population.
The main challenge for the protection of the Fakarava biosphere reserve is to find a balance between the economic, social and cultural needs of the inhabitants and the preservation of this fragile environment. The main economic activities in the region are fishing, aquaculture and tourism. People depend on these resources for their survival, but these activities can also have negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Among the many endemic species found on the atoll is the camouflage grouper, symbol of the Fakarava biosphere reserve. This fish, which is only found in the region, has developed a unique hunting technique by forming real walls to trap their prey. Protecting this fragile balance between species and the ecosystem as a whole is crucial to guarantee the survival of this exceptional biodiversity.
In conclusion, the Fakarava biosphere reserve is a treasure of nature, which reminds us how rich and fragile our planet is. Efforts to protect it must imperatively continue, involving local populations and promoting sustainable economic development. The survival of our common heritage and the future of future generations depends on it. So do not hesitate to commit to the preservation of this magnificent reserve and to support all the actions and initiatives put in place to preserve this unique place.
Terrestrial spaces
The land spaces of the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve are also very rich and varied. There are notably coastal forests, coconut groves, swamps as well as fine sandy beaches covered with coconut palms. These spaces are the refuge of many endemic birds, but also sea turtles and crabs.
Actions undertaken to preserve the biodiversity of the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve
Several actions are carried out within the reserve to protect animal and plant species and natural environments:
- Regulation of human activities: fishing, tourist activities and infrastructures are subject to strict regulations in order to preserve the ecological balance of the region.
- Surveillance and awareness: patrols are carried out regularly in the reserve to monitor the state of the ecosystems and ensure compliance with regulations. Local players and tourists are also made aware of the challenges of biodiversity conservation.
- Scientific research: research programs are carried out to better understand the species present in the reserve and the threats to them. The results of these studies are essential to better adapt protective measures.
The main activities to practice in the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve
There are several activities that visitors can practice in the reserve, respecting the environment and contributing to the preservation of natural spaces and the species present:
- Scuba diving and snorkeling: these activities allow you to discover the richness of the coral reefs and observe the many species of fish, turtles and sharks.
- Hiking: visitors can walk on the white sand beaches, in the coconut palm forests or along the lagoons to discover an incredibly rich fauna and flora.
- Boat trips: boat trips are ideal for observing birds and marine animals from the surface of the water, but also for going from one atoll to another and exploring deserted islands.
In conclusion, the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve is a real treasure of nature and a paradise for lovers of fauna and flora. The efforts made to preserve its ecosystems and the species that live there make this region a model of environmental management and protection.
FAQs:
1. Where is the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve located?
The Fakarava Biosphere Reserve is located in the Tuamotu Archipelago, in French Polynesia.
2. What area does the Fakarava Biosphere Reserve cover?
The reserve covers a maritime area of about 5.7 million square kilometers, encompassing all the atolls of the commune of Fakarava.
3. What are the main activities to practice in the reserve?
The main activities are scuba diving, snorkeling, hiking and boat trips.
4. What actions are taken to protect the biodiversity of the reserve?
The main actions are the regulation of human activities, the surveillance and awareness of inhabitants and tourists, as well as the promotion of scientific research.